A Fresh Look at InfiniBand
Posted by Frank Yang on Mar 28, 2022

InfiniBandTM has been on the market for more than two decades. Now that there have been new developments in 200G/400G link speeds, it’s worth taking a fresh look at InfiniBand.
What is InfiniBand?
According to InfiniBand Trade Association (IBTA), InfiniBand (IB) is “an industry-standard specification that defines an input/output architecture used to interconnect servers, communications infrastructure equipment, storage and embedded systems.”
InfiniBand’s low-latency, highly efficient communications make it suitable for supporting latency and loss-sensitive applications, which include high-performance computing (HPC) clustering or supercomputing.
Which applications does InfiniBand support?
Some HPC application examples are high-frequency trading, weather prediction, computational fluid dynamics simulation, and scientific research.
HPC clusters typically have many servers (often called “nodes”) and, in general, most of these nodes would be configured identically. The cluster may look like a single computer from the outside; however, its inside architecture is very complex.
While the terms of HPC “clustering” and “supercomputing” are often interchangeable, HPC is utilized to perform large scale of computing or data processing workloads.
What’s new with InfiniBand?
In recent years, machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytic workloads have fueled IB’s growth in hyperscale and cloud providers.
Nvidia Mellanox, a leading InfiniBand vendor, highlighted that demands for AI were surging, driven by hyperscale and cloud scale-out in its earnings release for Q3 fiscal year 2021. Intel, another leading IB vendor, also highlighted its processor architectural shifts to accelerate AI, HPC and advanced analytic workloads in its Q3 2021 financial reports.
IB continues to power supercomputing applications. IBTA reported that 200 gigabit per second high data rate (HDR) InfiniBand accelerates 31% of the new IB systems on the top 500 supercomputer list at the end of 2019. And InfiniBand powered 46 of the top 100 supercomputers on that list.
What are InfiniBand hardware subsystems?
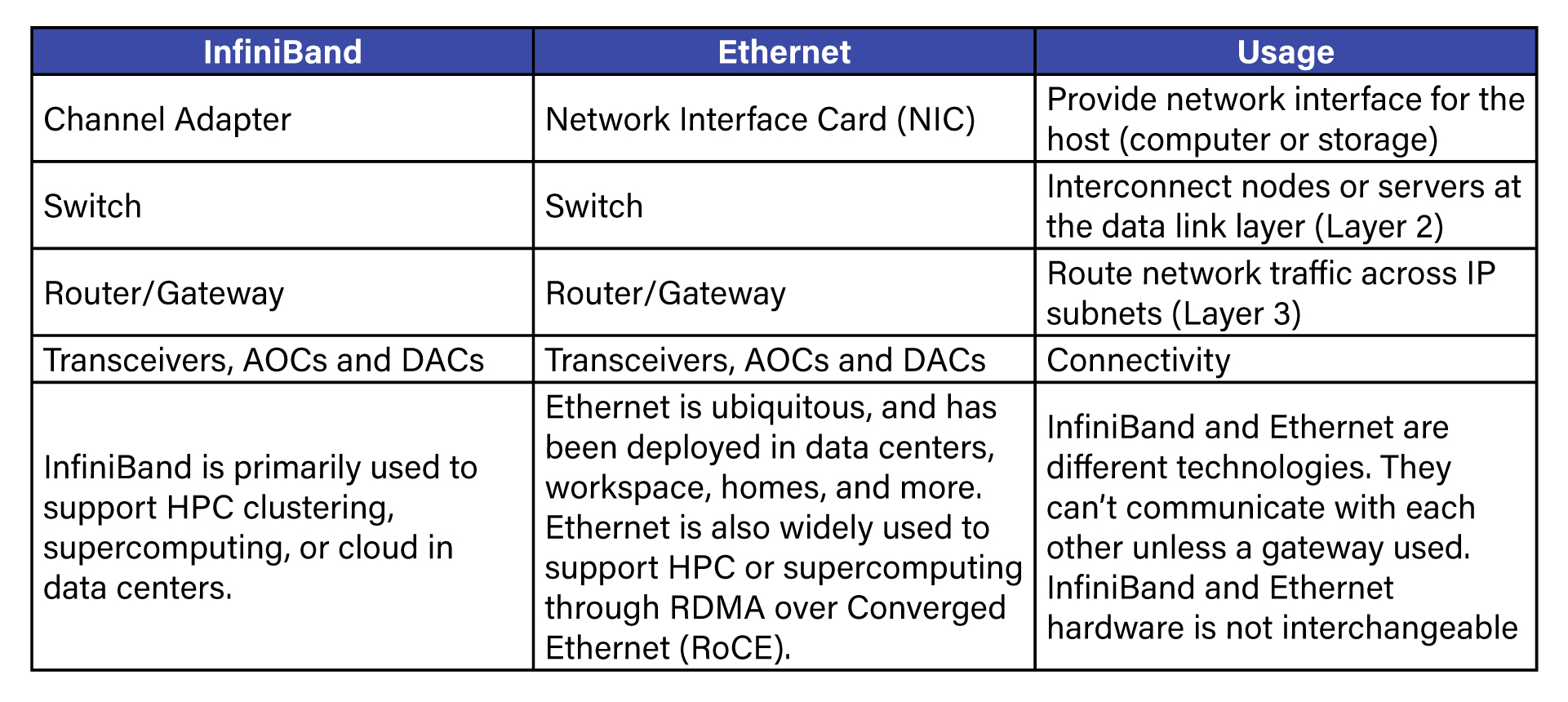
IB network subsystems are listed along with Ethernet for a quick reference purpose. Although they are architecturally similar, InfiniBand and Ethernet are different technologies.
What is defined in the InfiniBand Physical layer?
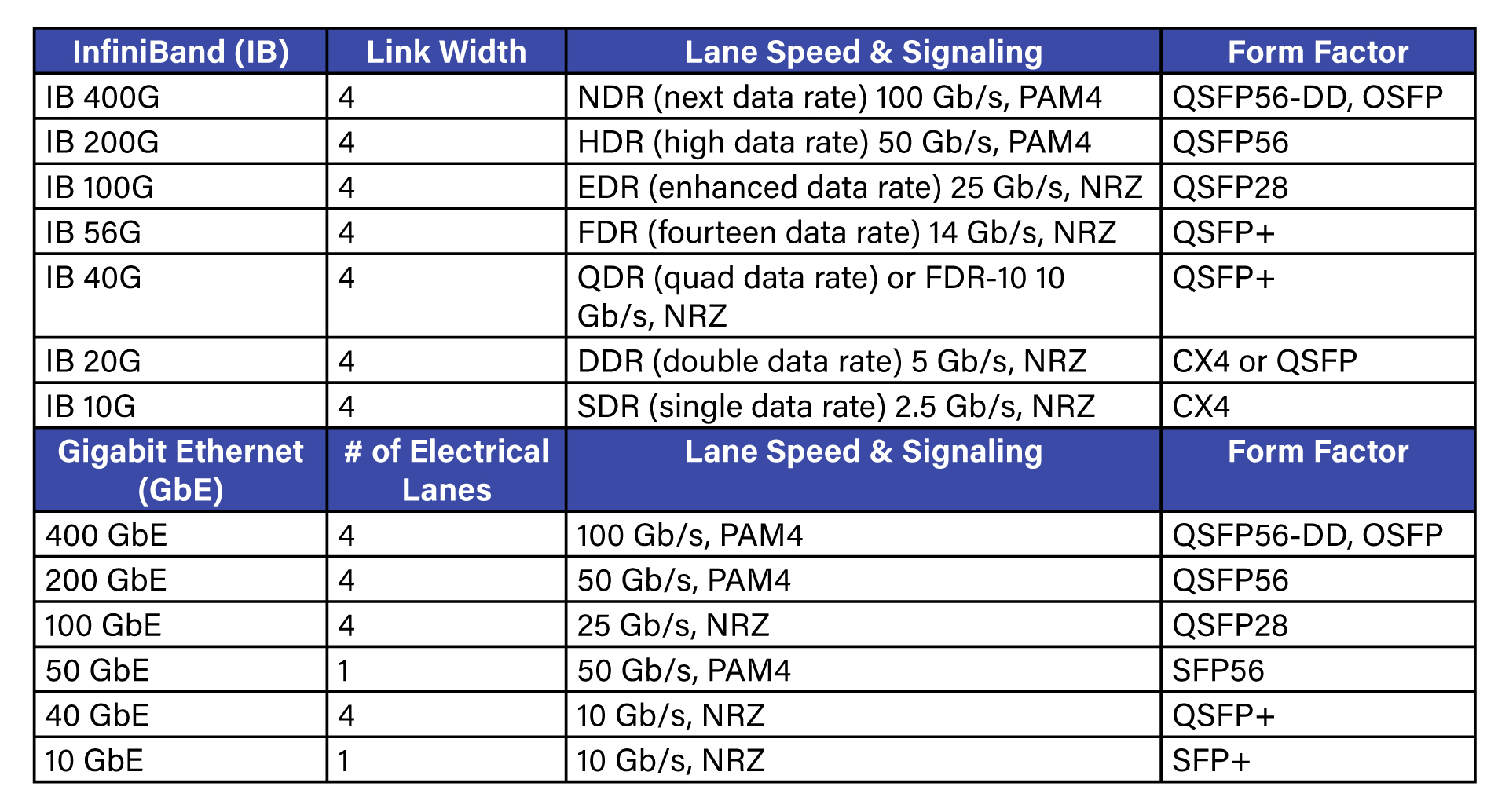
IB specifies link widths and the signaling rate for encoded data on the media at the physical layer. InfiniBand’s link widths have the options of 1x, 2x, 4x, 8x and 12x. The data rate (for example: HDR, EDR, etc.) spreads from the legacy 2.5 Gb/s to the most recent 100 Gb/s.
The effective link bandwidth is simply the link width times the data rate. For example, HDR itself represents the speed of 50 Gb/s per lane. The market term “InfiniBand HDR 200G” implies the link width of 4x running at the lane speed of 50 Gb/s. Similarly, “InfiniBand EDR 100G” means link width of 4x running at 25 Gb/s in each lane.
It’s worth reiterating that IB data rate names represent the speed of individual lane, not the aggregated effective link bandwidth.
Although InfiniBand specifies multiple link widths, the following table only lists the predominant one 4x for simplicity.
Note:
- QSFP stands for Quad Small Form-Factor Pluggable. DD means Double Density. And SFP is for Small Form-Factor Pluggable.
- The “56” (or ”28”) in QSFP56 (or QSFP28) indicates the maximum speed of 56 (or 28) Gb/s of individual electrical lane, representing the nominal data rate of 50 (or 25) Gb/s.
- NRZ stands for Non-Return to Zero. NRZ transmits digital data through two amplitude levels, one representing a digital “1” and the other representing a digital “0”.
- PAM4 stands for Pulse Amplitude Modulation 4. PAM4 transmits digital data through four amplitude levels, each level representing the combinations of two digits of “0” and “1”.
How are InfiniBand networks deployed?
The InfiniBand-based networking fabric typically is deployed in data centers. IB switches can be placed at the top of the server rack (ToR) or the end of the server cabinet row (EoR) -- like Ethernet switches.
In the ToR deployment, InfiniBand Direct Attach Cables (DACs) can be a good choice for connecting the IB ToR switch to the host channel adapter (HCA) installed in the node (server or storage).
In the EoR deployment, InfiniBand Active Optical Cables (AOCs) can be a good choice to connect the IB EoR switch to the node or server.
Call your Approved Networks representative to see how we can help you with your next InfiniBand project.